
What is Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)

If you are here reading this blog, then I guess either you are a business owner or a marketer or probably someone who knows all too well how difficult it is to acquire new customers. It’s essential to any growing company, but it can also be a constant source of headaches and financial strain.
What if I tell you that this customer acquisition cost is a goldmine of insights that has great potential to change your company completely? That’s the power of understanding and optimizing your customer acquisition cost (CAC).
CAC is one of the most important – yet frequently overlooked KPI of a business that aims to grow in its market. It stands for the average expenses you bear to acquire a new client, and it directly affects your long-term success, profitability, and scalability.
This blog focuses on the CAC calculation and its importance, but to understand customer acquisition, check out our separate post covering the entire customer acquisition process.
What is Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer acquisition cost is the cost a company bears to acquire a new customer. It includes the marketing, sales, and other related costs. Understanding the CAC of your business helps evaluate the efficiency of your customer acquisition strategies and improve profitability.
Related Read: What is Customer Acquisition
How to Calculate Customer Acquisition Cost?
CAC equation is the total amount spent on sales and marketing and other resources used to acquire new customers divided by the total number of customers acquired.
(Sales Expenses + Marketing Expenses) ÷ Number of New Customers Acquired = Customer Acquisition Cost

A lower CAC is desirable because it means you are spending less money on your efforts to acquire new customers.
If customer acquisition cost is greater than the revenue earned, then it’s a red flag – it means your customer acquisition strategies are either working poorly or are designed poorly. And if it keeps on going for a longer time, you are likely to go out of business – which we do not want at all.
Example of CAC Calculation
Let’s understand this by an example. Consider you acquired 20 new customers by spending $700 in marketing and $300 in sales.

It means that you spent $50 on each new customer. Now if these 20 customers earn you revenue of $3000 in say a month, you are doing well since your CAC $1000 is less than the revenue earned from these customers.
Types of Cost to Calculate CAC
There are several types of costs included in the “Total Sales and Marketing Costs” part of the CAC formula. Here’s a list so you can identify them for accurate CAC figures:
Advertising Costs
Costs for running ads (online, print, TV, radio, etc.).
Pay-per-click (PPC) campaigns, social media ads, display ads, and other paid digital marketing efforts are also included in advertising costs.
Marketing and Promotional Costs
Some of these costs include the cost of content marketing efforts, sponsorships, partnerships, and events for brand promotion.
Sales Team Salaries and Commissions
Include salaries, commissions, and bonuses for the sales team. Any benefits and other compensations given to the sales force are also considered in the CAC formula.
Marketing Staff Salaries
Salaries and wages of employees in the marketing department or any benefits like TADA associated with marketing personnel.
Types of Costs from Paid Tools
This includes the cost of tools that you buy to help your teams work efficiently e.g., costs of customer relationship management software, marketing automation platforms, analytics tools, etc.
Production Cost
It includes all the costs you need to create your product or service.
Creative Costs
Every cost that you bear to create content for your business falls under creative costs. This includes fees for graphic designers, videographers, and content creators, costs for creating ads, promotional materials, and marketing campaigns or even buying food for your teams.
Agency or Contractor Fees
These are fees paid to external agencies, consultants, or freelancers to help with marketing or sales. It is the cost of outsourced content creation, public relations, and advertising campaigns.
Training and Development
These are the costs related to training sales and marketing teams - Conferences, seminars, and workshops attended to improve skills and processes.
Inventory Overhead Costs
These include the costs of warehouse space, utilities, transportation, and other general overhead costs if you are in retail business. But SaaS business overheads involve software upgrades for customer satisfaction.
You may adjust the components of CAC depending on how you allocate resources to sales and marketing; however, the goal is to include all relevant expenses related to customer acquisition.
What is the Average Customer Acquisition Cost?
The average CAC also varies by industry, business size and strategy. For instance, the CAC for an e-commerce company may differ from that of a SaaS business. Some industries like SaaS tend to have higher CAC due to the complexities of customer onboarding, whereas retail or B2C companies might experience lower CAC due to more direct sales methods.
Understanding the average CAC in your industry can provide a useful benchmark for your efforts.
What is a Good Customer Acquisition Cost?
There is no one-size-fits all answer to what a “GOOD” CAC is because it depends on the market, your business model and customer lifetime value (CLTV). However, oftentimes, a “good CAC” is defined by how it compares to your CLTV.
Ideally speaking, for long-term profitability, your CLTV should be higher than your CAC. A commonly recommended ratio is 3:1, meaning your customer should generate three times the value of what it costs to acquire them. Anything above this ratio is brilliant, and anything below this ratio is a red flag.

Why Compare CAC to LTV
Customer Lifetime Value is the revenue that you acquired from a customer during their time of business with you. Mature businesses have a high LTV since their LTV strategies are well-optimized and are customer-centric, and their customer acquisition cost is low.
You will be surprised to know what insights you get when both of these metrics are read together. For example, you can get to answer these questions in granular ways while assessing product performance:
By product: What is the profitability of Product A vs. Product B in driving revenue?
By product variant: What is the profitability of the premium version vs. the standard version of Product A?
By feature: What is the impact of adding Feature X on Product A’s profitability compared to Product B’s equivalent feature?
By category: How does the profitability of electronics compare to clothing in my product lineup?
Similar approach can be adopted for other areas of your business but mind it, don’t get caught up in too many details. It would not be wise to chase growth via acquisition when you can do the same via innovation or retention.
The CAC to Customer LifeTime Value Ratio
The CAC to CLTV ratio is the only calculation that tells you how much revenue wise value a customer brings to your business as compared to the cost you bear to acquire them.
The ideal time period to calculate customer value is one year. So you should get a 3:1 ratio by the end of a year when calculating CLTV to CAC ratio. It means that the lifetime value of each customer should be three times the cost of acquisition. Here’s how you can calculate it.
CAC LTV ratio = LTV ÷ CAC

Here is a basic example to calculate this ratio.
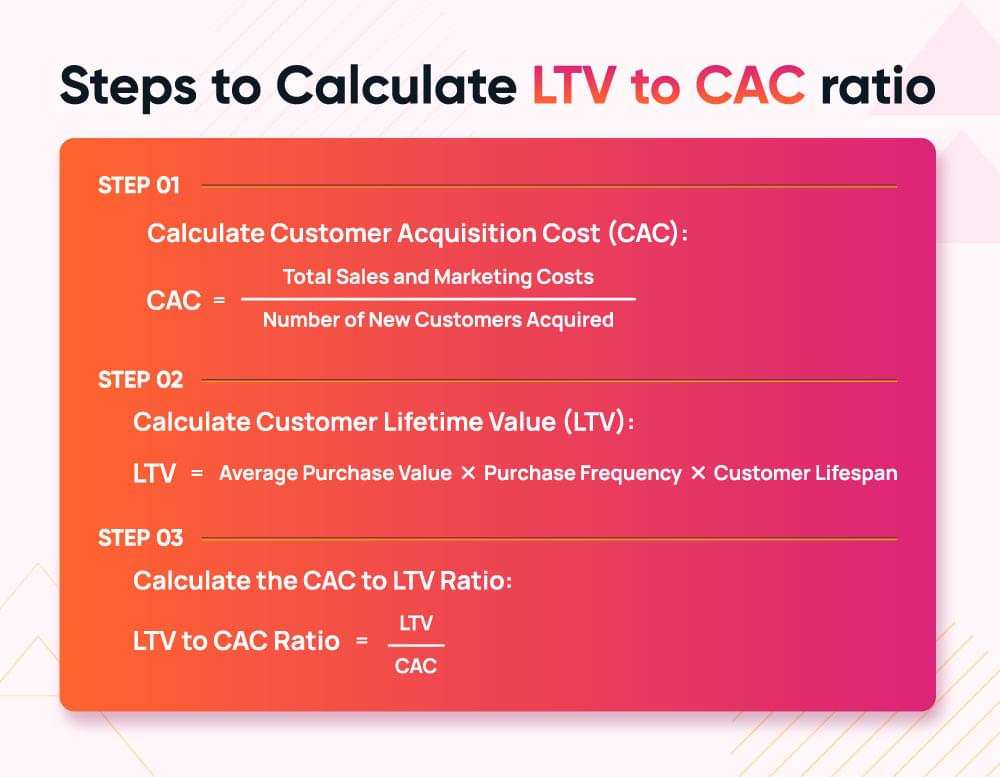
Example:
- CAC: $50
- LTV: $150
CAC to LTV ratio=150 ÷ 50 = 3:1
This means for every $1 spent on acquisition, the customer brings $3 in value.
What Effects Customer Costs by Industry
Different industries have different reasons for their high or low CAC e.g.
E-commerce: Lower CAC due to the direct nature of sales and online marketing.
SaaS industry: Higher CAC because of the complex sales process and extended customer onboarding.
Financial Services: High CAC due to strict regulatory requirements and longer sales cycles.
But some factors remain common in every industry especially when customer is aware of your business.
What is the cost of your product?
How soon a sale closes?
How long does a customer stay your customer?
How frequent are the repeat purchases of a customer?
These are simple yet powerful factors as they help smoothly yield your CAC into acquisition.
How to Improve CAC – Here’s How Reducing Customer Churn Can Help
Improving efficiency in marketing and sales efforts can help lower CAC. But reducing your churn can prove to be the real deal.
“CRM has come to be recognized as the foundation of contemporary marketing strategy”, said RJ Baran and RJ Galka in their book “Customer Relationship Management: the foundation of contemporary marketing strategy” while highlighting the importance of customer acquisition.
Reduced Churn = Increased customer lifetime value (LTV) + Loyal Customers + Repeat Buyers
Customer acquisition via Word-of-mouth and referrals
Reduced customer onboarding costs
Increased operational efficiency
Here’s a guide to Customer retention management for new and existing customers. Platforms like Churnfree can help you retain customers and improve CAC. You will find top-quality customer feedback forms andretention flows to reduce churn rate of your business. here are some other reads to help you understand churn better.
5 Simple Ways to Analyze Customer Churn Causes
Case study: How SubtitleBee reduced churn by 40%
Reduce Churn SaaS in 2024. Methods that actually work!
How To Deal With Angry Customers
B2B Customer Journey: Stages, Map, Templates and Examples
Here are some other effective strategies to improve CAC.
- Know your Target Audience and understand buyer personas
- Invest in your website to optimize its Conversion rate (CRO)
- Create high-quality blogs, videos, and white papers to generate organic traffic.
- Offer Referrals and Discounts to new customers.
- Work to improve Return on Investment (ROI) of customer acquisition campaigns.
- Do not underestimate the power of Customer Services Team

What is Organic CAC
Organic CAC refers to the cost of acquiring customers through internal, self-sustaining methods such as content marketing, SEO, referrals, etc.
It is usually associated with genuine job creation and long-term value creation. Organic CAC is considered more sustainable and cost-effective in the long run.
For example, SaaS company like ChurnFree.com grows its customer base through content marketing. By consistently publishing high-quality blog posts, SEO-optimized articles, and social media content, the company attracts visitors organically over time.
What is Inorganic CAC
Inorganic CAC also called Paid CAC refers to the cost of acquiring customers through external, non-organic methods such as advertising, partnerships, acquisitions, etc.
Paid CAC often involves higher upfront costs but can provide faster customer growth. It can help achieve economies of scale and diversification, but may also come with challenges like integration, culture clashes, and increased variable costs.
Example of inorganic CAC can be when A retail company acquires customers through paid advertising on Google Ads and Facebook Ads.
Why Calculate Acquisition Cost
Customer Acquisition is the growth of your business, but growth does not come free – it has a cost – CAC
When you spend on growth you need to keep your eyes open. The goal is to find a balance between growth and cost of growth.
A balanced CAC ensures that you’re not overspending to gain customers. When you efficiently manage CAC, it helps in allocating your business resources wisely. It improves return on investment (ROI) figure, and ensures long-term profitability when aligned with customer lifetime value (LTV). This balance is key to scaling in a cost-effective way.

I hope this article helped you understand customer acquisition cost. For more related blogs visit Churnfree Blog.


