
Customer Acquisition Cost for SaaS (CAC SaaS) Examples

Customer acquisition cost for SaaS(CAC) is a metric that has been growing with online businesses mostly SaaS-based and web-based advertising campaigns that needs tracking.
As you may know, CAC is the cost of convincing a potential user to buy a product or service—offering clear view on how much it costs to acquire a customer and can help businesses determine the effectiveness of their sales and marketing efforts. By comparing CAC to the average lifetime value of a customer, companies can also determine if their customer acquisition efforts are profitable.
Improving CAC requires a holistic approach that takes into account various factors such as optimizing marketing channels, improving conversion rates, and reducing customer churn. Targeting the right audience with the right message through effective marketing campaigns can help reduce CAC. Improving the user experience and providing excellent customer service can also increase conversion rates and reduce customer churn, thereby improving CAC.
The read of this blog will elaborate the CAC metric in SaaS industry in more detail, how you can measure it, and what steps you can take to improve it.
What is Customer Acquisition Cost for SaaS?
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) for a SaaS business can therefore be defined as the total costs of acquiring a customer. It includes all the sales and marketing expenses associated with bringing in new customers.
The cost per customer acquisition (CAC) metric is important for two key parties: company and shareholders. For early stage individuals in business, use CAC to assess new SaaS-based businesses leveraging on the internet space and their scalability. It explains that with the help of comparing the costs connected with the customer acquisition and revenue investors can determine the exact level of profitability of a certain company.
For example in the upstream oil market the extractive cost may be above the going market price per barrel if the oil is located in an area that requires a lot of development to access.
SaaS based business operate under the same lens at the core of its functioning. Another party that has a more informed view of the CAC metric is the SaaS businesses or marketing specialists. From this metric, they are able to effectively decide how best to reinvest on advertising and enhance the return on investment. In simpler terms, if it is possible for a company to increase its revenue from a customer at a faster pace than the cost of acquiring the customer, then the company’s profitability is set to increase.
Investor need to apply the required resources in a company while partners are interested in the growth of the company. The enhanced profit margins may be used to come up with superior value propositions to customers thereby enjoying a better position in the market.
How to Calculate CAC SaaS?
CAC, otherwise known as cost per customer acquisition is also an important metric which lost should find extremely useful in estimating the amount of money a company spends to acquire a new customer. Total marketing, advertising and other expenses incurred to gain customers is divided in this formula by the number of customers gained in a particular period of time.
CAC Formula = Cost of Sales + Cost of Marketing / New Customer Acquired
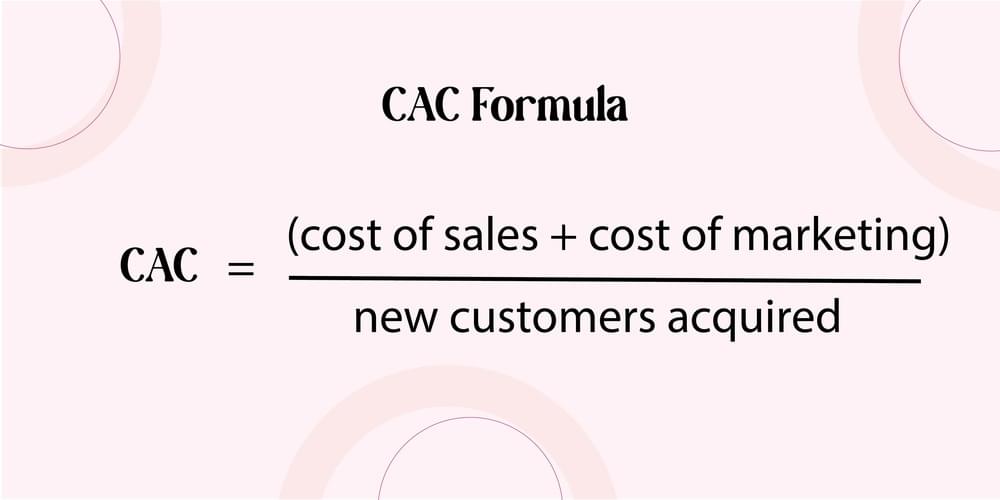
CAC, otherwise known as cost per customer acquisition is also an important metric which lost should find extremely useful in estimating the amount of money a company spends to acquire a new customer. Total marketing, advertising and other expenses incurred to gain customers is divided in this formula by the number of customers gained in a particular period of time.
For example, it may cost $100 annually to advertise for a company ‘s annual marketing budget and get 100 customers per year, CAC equals $1. 00. However, one should not forget that there are certain factors which influence the reliability of this indicator.
For instance, a firm may have embarked on marketing of a new region that may not produce results at a later date or SEO that may prove unprofitable in the long run. Such cases can act as a distortion factor when determining the CAC in a relationship. Hence we need to do many variations to allow for such eventualities.
But, let’s give two examples of the simplest CAC calculation Initial Cost / Sale. Here Company 1 has a low value and Company 2 has a high value.
Example 1: Let a given company invested $100,000 in the marketing channel and attained 500 customers on an annual basis. If such a balance sheet were applied with this company, the CAC would be $200. This is regarded as a bad indicator, and the company can possibly have to re-strategise how it will lower their CAC.
Example 2: For instance, another company invested $100, 000 on marketing and obtained a thousand customer annually. If this were to be the case, the CAC for this company would be a hundred dollars. This is a good one, and it has to be the company’s marketing strategy to ensure that it gets even more customers with a lower cost.
Calculation Example
Let us again consider another example in order to illustrate how a firm can determine the cost per acquiring customer (CAC). Looking at this example, this case will consider a cloud based customer relationship management (CRM) software firm. The software is sold via the internet, and the clients do not need any assistance most of the time, so the distribution costs are low.
Also, it has been able to maintain its customers because migration of contacts, tasks, and events from one CRM software to another is tiresome. The company has implemented strategies that would increase its ranking with search engines and has ‘sales support specialists’ who operate from call centers located in a rural Mid-Vwest town and are paid at minimum wages.
The company has also made regular strategic partnerships that seal a constant line of customers for the business. For that matter, it only spends $2 to obtain a new customer who has an estimated value of $2000 throughout his/her lifetime. Let’s take a closer look at the calculation:Let’s take a closer look at the calculation:
- Total cost of sales support call centers for new customers: $ 1,000,000 per year
- Total cost paid to strategic alliance partners per customer: $ 1.00
- Total monthly spending on search engine optimization: $20000/YR
Total new customers generated in the year: 1,020,000Customer acquisition cost: ($1,020,000 / 1,020,000 customers) + $1.00 per customer = $2.00Using a customer retention formula, this company has calculated its customer lifetime value (CLV) to be $2,000.This implies that for every $2 spent on acquiring a new customer, the company earns $2,000 in revenue. This is a promising sign for investors and indicates to the marketing team that the company’s system is effective.
However, it is important for one to understand that this formula may not hold for all organizations or fields. Other metrics like the return on investment (ROI) can be used to get a better understanding of the company’s performance.
Types of Costs to Include in a Cost Per Acquisition Formula
When calculating the cost per customer acquisition (CAC), it is important to include all relevant costs to get an accurate picture of the investment required to acquire a customer. Here are some of the types of costs that should be considered when calculating CAC:
- Marketing Costs: This includes all costs associated with marketing activities such as advertising, content creation, search engine optimization (SEO), email marketing, social media marketing, and events.
- Sales Costs: This includes all costs associated with the sales process, such as salaries and commissions for sales representatives, sales training, and software or tools used to manage the sales process.
- Overhead Costs: This includes all other indirect costs associated with acquiring a customer, such as rent, utilities, office supplies, and other general expenses.
- Technology Costs: This includes all costs associated with the technology used to acquire customers, such as website hosting, landing page software, email marketing software, and any other software or tools used to manage the marketing and sales process.
Cost Per Customer Acquisition Use Case Scenarios
For every business calculating cost per customer acquisition is different. Therefore it is important to know how to calculate CAC for different businesses. Once you understand how to calculate CAC, you may want to understand its impact on your business. Here are some use-case scenarios where understanding and managing CAC can make a significant impact:
- Startups: Keeping CAC low is essential for startups, especially in the early stages when cash flow is tight. A high CAC can quickly drain available resources, and it could take longer to achieve profitability. Startups should focus on cost-effective marketing channels and strategies, such as social media marketing, content marketing, and referral programs.
- SaaS Subscription-based businesses: CAC is essential for subscription-based businesses, where customer acquisition is just the beginning of the revenue stream. These businesses need to balance the cost of acquiring new customers with the expected revenue from their subscriptions. A high CAC can make it difficult to generate profit from subscriptions, so these businesses should focus on retaining customers for longer periods.
- E-commerce businesses: For e-commerce businesses, the CAC formula can be a bit more complex, as it needs to factor in the cost of goods sold (COGS) in addition to marketing and sales expenses. These businesses need to focus on improving their customers’ lifetime value (LTV), as a high LTV can offset a higher CAC.
- B2B companies: In B2B companies, the sales cycle can be longer, and there are often more decision-makers involved in the buying process. As a result, CAC can be higher for B2B companies. These companies should target the right customers and optimize their sales process to reduce the sales cycle length.
- High-growth companies: For high-growth companies, managing CAC becomes even more critical. As the company grows, it can become more difficult to maintain a low CAC while acquiring a high volume of customers. These companies should optimize their marketing channels and identify new channels for customer acquisition.
Customer Acquisition Cost Examples in SaaS Industry
Below are SaaS Industry CAC, providing an insight on how specific organizations control the costs of attaining customers.
Slack
Unlike most software and business solutions, Slack’s sales approach does not heavily depend on a direct sales force, instead, it employs the word-of-mouth advertising, viral adoption, and content marketing strategies. This enables the company to keep its CAC low and more manageable than is the norm with other enterprise SaaS companies. The key plan that slack has employed is to provide a freemium service whereby, users can begin using the product for free hence, it easy for small working groups to start using the product with the intention of progressing to the paid levels. The estimated CAC for Slack is approximately: **$2000” This is the result of Slack’s strategic and sustainable approach to get in touch with the needful market.
HubSpot
Thus, Hubspot, being the leader in inbound, or content marketing software, has much higher CAC due to content marketing, paid advertising, CRM, and salesforce purchases. Lead acquisition through inbound marketing method of HubSpot generates a lot of leads; however, the various stages in the sales funnel may require huge efforts in order to close them, therefore increasing acquisition cost. For its SMB customer segment, HubSpot’s CAC is assumed to lie in the range of $11,000 per customer. This higher cost is due to its call multi tier channel strategy and also due to its longer sales cycle especially for its enterprise customers.
Salesforce
Salesforce is one of the leading SaaS providers and it operates at the enterprise level which naturally yields high CAC. The company’s customer acquisition is through direct sales, it has a number of sales persons involved, their commission is high and the company targets long term contracts with customers, mostly businesses. Such enterprise arrangements usually entail more than one contact, consultation, and specially tailored onboard process, all of which are costly. We estimate annual customer acquisition cost for CAC of Salesforce to be between $15,000 and $20,000 per customer, this is because the sale to a customer especially a big organization is not a simple process, besides SalesForce’s business model depends on long-term versus short-term contracts.
Dropbox
Initially, the company experienced a low CAC and this was attributed to the fact that the company invested its resources in expanding sales through a referral program where users were awarded more storage space for every invite made by them. Such organic growth concept was useful in maintaining low early CAC below $300-$400 per customer when targeting the client on the consumer level. But as it moved to the business and enterprise SaaS market, it had to begin spending more on sales and marketing and thereby raised the CAC to $1000-$1500 per customer. This rise can be attributed to increase in cost relating to the segment targeting of bigger firms, which have higher revenue generation capabilities.
Zendesk
For instance, Zendesk that offers customer support solutions has comparable CAC values as any mid-tier SaaS companies. Marketing automation, customer success, programmes and a focused sales effort are dedicated to securing customers for the company. According to Zendesk, the estimated customer acquisition cost is about $10,000 especially for mid and enterprise market segments. They also usually need more attention during the onboarding process and hence are expensive to acquire.
Intercom
Intercom is about customer communication and messaging needs and solutions for those who need better communication tools for their business. This means that the company invests greatly in digital marketing and content as well as customer success. CAC at Intercom is from $500 to $2,000 per customer depending on the size of the customer that is being targeted. On the average, SMB customers are usually cheaper to acquire than the enterprise customers owing to the fact that enterprise customers usually require a more detailed selling approach and longer cycle duration to close deals.
CAC descriptive of the SaaS industry greatly differs in terms of the target market, sales strategy or model. Freemium and viral business models, including Slack and Dropbox, have a low CAC at the beginning for this reason; in contrast, Salesforce and HubSpot have a high cost since their companies sell to enterprises and require elaborate and lengthy sales funnels to close deals.
What About The Cost Per Customer Acquisition For Marketing Channel?
As a marketer, you’re likely interested in knowing each marketing channel’s customer acquisition cost (CAC). Understanding which channels have the lowest CAC can help determine where to focus your marketing spend. By allocating your budget to lower CAC channels, you can acquire more customers for the same amount.
The simplest way to calculate CAC is to collect all your marketing receipts for a specific period and add up the amounts by channel. For example, you can create columns for “PPC” or “Pay-Per-Click” and “Inbound Marketing Costs” and input the relevant expenses.
However, this approach can be problematic because it assumes that each channel is equally effective in acquiring customers. It can be difficult to determine which channel is responsible for which customers, especially if you run a limited test for one channel.
For instance, you have decided to run a PPC campaign under a budget of $10. Seeing the spreadsheet, it might appear that PPC is the most effective marketing channel due to its exceptionally low cost of customer acquisition (CAC). However, you may want to wait before doubling down on PPC; as for now, you don’t have a comprehensive picture of the channel’s performance under the given time.
For e-commerce businesses selling physical products, it is very easy to know the results a PPC campaign may generate—for instance, leading to direct sales. To better understand each channel’s effectiveness, you can use tools like customer analytics to trace paying customers back to their last “touch attribution source”. This will help you identify the last channel the customer visited before making their first purchase with your online business
.For instance, if a customer found your business through an organic search, you would know that SEO was responsible for their acquisition.
Some marketers believe that each marketing channel supports the next channel in a combined effort, and all channels work together to bring in customers. Others prefer to rely on the last-touch attribution model for their CAC calculations.
How can you reduce customer acquisition cost for SaaS?
Here Are some ways to improve customer acquisition cost for SaaS:
- Refine your targeting: Ensure that your firm’s marketing campaigns are directed towards the right people. Therefore it is important to research the market so as to identify the target customers and make the appropriate changes in the marketing message and advertising material.
- Focus on content marketing: Create good, and relevant information that helps the target audience and also makes the brand an authority in the niche. It can also be useful in popularizing a particular product and attracting individuals who could become its clients and bringing them to your site.
- Social media presence: People are highly active on social media and therefore it is a good source to engage the potential customers and to popularize the brand. Target customers through the social pages and market your products and services through the social media marketing campaigns.
- Optimize your website: In this case, ensure that you have designed you website for search engines as well as for the users. This will help boost your search engine visibility and potential of getting new customers to visit your site.
- Optimize your conversion rate: Streamline your website and ensure that closing visitors and turning into leads and customers is easy. Ensure your site is mobile responsive, tinker with the website content and find ways of making the purchasing funnel seamless for customers.
- Add value: Enhance the customer value by identifying their wants, and as a result offering them what they would find useful. Get feedback from your customers and incorporate it into your product line or additional features or products to which the customers can be loyal.
- Implement a customer referral program: This proves that customer referral programs are a good way through which firms can gain access to new clients at a cheaper price. Referral marketing is also beneficial to your business for it helps you attain new customers at a cheaper rate and retain customer loyalty.
- Improve your sales funnel: If you have recently optimized your website for search engines, go through the sales funnel critically to determine where b2b prospects may be leaving. Any irregularities that may have affected your customers’ purchasing decisions must be ironed out and the entire process made easier and convenient for the clients.
- Streamline your sales cycle: Utilize customer relationship management (CRM) and prospecting to reach out to the qualified leads to be able to post less cycle time. This will create a positive effect on the amount of sales that you will be able to coax over time hence bringing down the CAC.
What is a good CAC for SaaS?
By definition, the best customer acquisition cost for SaaS varies depending on the company’s revenue model and industry type. Nevertheless, the majority of SaaS businesses try to achieve such a CAC to lifetime value ratio, which is 3:1.
What is a good LTV ratio fredor SaaS?
The ideal LTV to CAC ratio for SaaS businesses is believed to range between 3:1 and 5:1. This means that cost per acquisition of a new customer (CAC) ideally should be thrice to five times the total revenues expected to be generated from the same customer in future (LTV).
Bottom-Line
I hope this article helped you understand and calculate customer acquisition cost for SaaS.
Related Read:


